构建 MCP 服务器
在本教程中,我们将构建一个简单的 MCP 天气服务器并将其连接到一个主机——Claude 桌面版。
我们将要构建的内容
我们将构建一个暴露两个工具的服务器:get_alerts 和 get_forecast。然后将服务器连接到 MCP 主机(在本例中为 Claude 桌面版):
服务器可以连接到任何客户端。我们在这里选择 Claude 桌面版是为了简单起见,我们也提供了关于构建你自己的客户端的指南,以及其他客户端列表。
MCP 核心概念
MCP 服务器可以提供三种主要类型的能力:
本教程将主要关注工具。
让我们开始构建天气服务器!你可以在这里找到我们将要构建的完整代码。
前置知识
本快速入门假设你熟悉:
- Python
- LLM(如 Claude)
MCP 服务器中的日志记录
在实现 MCP 服务器时,请注意如何处理日志记录:
**对于基于 STDIO 的服务器:**切勿写入标准输出。这包括:
- Python 中的
print()语句 - JavaScript 中的
console.log() - Go 中的
fmt.Println() - 其他语言中类似的标准输出函数
写入标准输出会破坏 JSON-RPC 消息并导致服务器崩溃。
**对于基于 HTTP 的服务器:**标准输出日志是可以的,因为它不会干扰 HTTP 响应。
最佳实践
- 使用写入 stderr 或文件的日志库。
- 对于 Python 要特别小心 -
print()默认写入标准输出。
快速示例
# ❌ 错误(STDIO)
print("Processing request")
# ✅ 正确(STDIO)
import logging
logging.info("Processing request")系统要求
- 安装 Python 3.10 或更高版本。
- 必须使用 Python MCP SDK 1.2.0 或更高版本。
设置环境
首先,让我们安装 uv 并设置我们的 Python 项目和环境:
curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | shpowershell -ExecutionPolicy ByPass -c "irm https://astral.sh/uv/install.ps1 | iex"之后务必重启终端,以确保 uv 命令被识别。
现在,让我们创建并设置我们的项目:
# Create a new directory for our project
uv init weather
cd weather
# Create virtual environment and activate it
uv venv
source .venv/bin/activate
# Install dependencies
uv add "mcp[cli]" httpx
# Create our server file
touch weather.py# Create a new directory for our project
uv init weather
cd weather
# Create virtual environment and activate it
uv venv
.venv\Scripts\activate
# Install dependencies
uv add mcp[cli] httpx
# Create our server file
new-item weather.py现在让我们开始构建服务器。
构建服务器
导入包和设置实例
将这些添加到 weather.py 的顶部:
from typing import Any
import httpx
from mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCP
# Initialize FastMCP server
mcp = FastMCP("weather")
# Constants
NWS_API_BASE = "https://api.weather.gov"
USER_AGENT = "weather-app/1.0"FastMCP 类使用 Python 类型提示和文档字符串来自动生成工具定义,使得创建和维护 MCP 工具变得容易。
辅助函数
接下来,让我们添加辅助函数,用于从国家气象局 API 查询和格式化数据:
async def make_nws_request(url: str) -> dict[str, Any] | None:
"""Make a request to the NWS API with proper error handling."""
headers = {"User-Agent": USER_AGENT, "Accept": "application/geo+json"}
async with httpx.AsyncClient() as client:
try:
response = await client.get(url, headers=headers, timeout=30.0)
response.raise_for_status()
return response.json()
except Exception:
return None
def format_alert(feature: dict) -> str:
"""Format an alert feature into a readable string."""
props = feature["properties"]
return f"""
Event: {props.get("event", "Unknown")}
Area: {props.get("areaDesc", "Unknown")}
Severity: {props.get("severity", "Unknown")}
Description: {props.get("description", "No description available")}
Instructions: {props.get("instruction", "No specific instructions provided")}
"""实现工具执行
工具执行处理器负责实际执行每个工具的逻辑。让我们添加它:
@mcp.tool()
async def get_alerts(state: str) -> str:
"""获取美国州的天气警报。
Args:
state: 两位数的美国州代码(例如 CA、NY)
"""
url = f"{NWS_API_BASE}/alerts/active/area/{state}"
data = await make_nws_request(url)
if not data or "features" not in data:
return "Unable to fetch alerts or no alerts found."
if not data["features"]:
return "No active alerts for this state."
alerts = [format_alert(feature) for feature in data["features"]]
return "\n---\n".join(alerts)
@mcp.tool()
async def get_forecast(latitude: float, longitude: float) -> str:
"""Get weather forecast for a location.
Args:
latitude: Latitude of the location
longitude: Longitude of the location
"""
# First get the forecast grid endpoint
points_url = f"{NWS_API_BASE}/points/{latitude},{longitude}"
points_data = await make_nws_request(points_url)
if not points_data:
return "Unable to fetch forecast data for this location."
# Get the forecast URL from the points response
forecast_url = points_data["properties"]["forecast"]
forecast_data = await make_nws_request(forecast_url)
if not forecast_data:
return "Unable to fetch detailed forecast."
# Format the periods into a readable forecast
periods = forecast_data["properties"]["periods"]
forecasts = []
for period in periods[:5]: # Only show next 5 periods
forecast = f"""
{period["name"]}:
Temperature: {period["temperature"]}°{period["temperatureUnit"]}
Wind: {period["windSpeed"]} {period["windDirection"]}
Forecast: {period["detailedForecast"]}
"""
forecasts.append(forecast)
return "\n---\n".join(forecasts)运行服务器
最后,让我们初始化并运行服务器:
def main():
# Initialize and run the server
mcp.run(transport="stdio")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()你的服务器已完成!运行 uv run weather.py 来启动 MCP 服务器,它将监听来自 MCP 主机的消息。
现在让我们从现有的 MCP 主机 Claude 桌面版测试你的服务器。
使用 Claude 桌面版测试服务器
Claude 桌面版尚不支持 Linux。Linux 用户可以继续阅读构建客户端教程,构建一个连接到我们刚刚构建的服务器的 MCP 客户端。
首先,确保已安装 Claude 桌面版。你可以在此处安装最新版本。如果已有 Claude 桌面版,请确保更新到最新版本。
我们需要为要使用的任何 MCP 服务器配置 Claude 桌面版。为此,请在文本编辑器中打开 ~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json 中的 Claude 桌面版应用配置。如果文件不存在,请确保创建它。
例如,如果安装了 VS Code:
code ~/Library/Application\ Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.jsoncode $env:AppData\Claude\claude_desktop_config.json然后,你将在 mcpServers 键中添加服务器。只有在至少有一个服务器正确配置后,MCP UI 元素才会显示在 Claude 桌面版中。
在这种情况下,我们将像这样添加单个天气服务器:
{
"mcpServers": {
"weather": {
"command": "uv",
"args": [
"--directory",
"/ABSOLUTE/PATH/TO/PARENT/FOLDER/weather",
"run",
"weather.py"
]
}
}
}{
"mcpServers": {
"weather": {
"command": "uv",
"args": [
"--directory",
"C:\\ABSOLUTE\\PATH\\TO\\PARENT\\FOLDER\\weather",
"run",
"weather.py"
]
}
}
}你可能需要在 command 字段中放置 uv 可执行文件的完整路径。你可以通过在 macOS/Linux 上运行 which uv 或在 Windows 上运行 where uv 来获取此路径。
确保传入服务器的绝对路径。你可以通过在 macOS/Linux 上运行 pwd 或在 Windows 命令提示符上运行 cd 来获取此路径。在 Windows 上,请记住在 JSON 路径中使用双反斜杠 (\\) 或正斜杠 (/)。
这告诉 Claude 桌面版:
- 有一个名为 “weather” 的 MCP 服务器
- 通过运行
uv --directory /ABSOLUTE/PATH/TO/PARENT/FOLDER/weather run weather.py来启动它
保存文件,并重启 Claude 桌面版。
让我们开始构建天气服务器!你可以在这里找到我们将要构建的完整代码。
前置知识
本快速入门假设你熟悉:
- TypeScript
- LLM(如 Claude)
MCP 服务器中的日志记录
在实现 MCP 服务器时,请注意如何处理日志记录:
**对于基于 STDIO 的服务器:**切勿写入标准输出。这包括:
- Python 中的
print()语句 - JavaScript 中的
console.log() - Go 中的
fmt.Println() - 其他语言中类似的标准输出函数
写入标准输出会破坏 JSON-RPC 消息并导致服务器崩溃。
**对于基于 HTTP 的服务器:**标准输出日志是可以的,因为它不会干扰 HTTP 响应。
最佳实践
- 使用写入 stderr 或文件的日志库,例如 Python 中的
logging。 - 对于 JavaScript 要特别小心 -
console.log()默认写入标准输出。
快速示例
// ❌ 错误(STDIO)
console.log("Server started");
// ✅ 正确(STDIO)
console.error("Server started"); // stderr 是安全的
系统要求
对于 TypeScript,确保已安装最新版本的 Node。
设置环境
首先,让我们安装 Node.js 和 npm(如果尚未安装)。你可以从 nodejs.org 下载它们。 验证你的 Node.js 安装:
node --version
npm --version对于本教程,你需要 Node.js 版本 16 或更高版本。
现在,让我们创建并设置我们的项目:
# Create a new directory for our project
mkdir weather
cd weather
# Initialize a new npm project
npm init -y
# Install dependencies
npm install @modelcontextprotocol/sdk zod@3
npm install -D @types/node typescript
# Create our files
mkdir src
touch src/index.ts# Create a new directory for our project
md weather
cd weather
# Initialize a new npm project
npm init -y
# Install dependencies
npm install @modelcontextprotocol/sdk zod@3
npm install -D @types/node typescript
# Create our files
md src
new-item src\index.ts更新你的 package.json 以添加 type: “module” 和构建脚本:
{
"type": "module",
"bin": {
"weather": "./build/index.js"
},
"scripts": {
"build": "tsc && chmod 755 build/index.js"
},
"files": ["build"]
}在项目根目录中创建 tsconfig.json:
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "ES2022",
"module": "Node16",
"moduleResolution": "Node16",
"outDir": "./build",
"rootDir": "./src",
"strict": true,
"esModuleInterop": true,
"skipLibCheck": true,
"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true
},
"include": ["src/**/*"],
"exclude": ["node_modules"]
}现在让我们开始构建服务器。
构建服务器
导入包和设置实例
将这些添加到 src/index.ts 的顶部:
import { McpServer } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/mcp.js";
import { StdioServerTransport } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/stdio.js";
import { z } from "zod";
const NWS_API_BASE = "https://api.weather.gov";
const USER_AGENT = "weather-app/1.0";
// Create server instance
const server = new McpServer({
name: "weather",
version: "1.0.0",
});辅助函数
接下来,让我们添加辅助函数,用于从国家气象局 API 查询和格式化数据:
// Helper function for making NWS API requests
async function makeNWSRequest<T>(url: string): Promise<T | null> {
const headers = {
"User-Agent": USER_AGENT,
Accept: "application/geo+json",
};
try {
const response = await fetch(url, { headers });
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(`HTTP error! status: ${response.status}`);
}
return (await response.json()) as T;
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error making NWS request:", error);
return null;
}
}
interface AlertFeature {
properties: {
event?: string;
areaDesc?: string;
severity?: string;
status?: string;
headline?: string;
};
}
// Format alert data
function formatAlert(feature: AlertFeature): string {
const props = feature.properties;
return [
`Event: ${props.event || "Unknown"}`,
`Area: ${props.areaDesc || "Unknown"}`,
`Severity: ${props.severity || "Unknown"}`,
`Status: ${props.status || "Unknown"}`,
`Headline: ${props.headline || "No headline"}`,
"---",
].join("\n");
}
interface ForecastPeriod {
name?: string;
temperature?: number;
temperatureUnit?: string;
windSpeed?: string;
windDirection?: string;
shortForecast?: string;
}
interface AlertsResponse {
features: AlertFeature[];
}
interface PointsResponse {
properties: {
forecast?: string;
};
}
interface ForecastResponse {
properties: {
periods: ForecastPeriod[];
};
}实现工具执行
工具执行处理器负责实际执行每个工具的逻辑。让我们添加它:
// Register weather tools
server.registerTool(
"get_alerts",
{
description: "获取州的天气警报",
inputSchema: {
state: z
.string()
.length(2)
.describe("Two-letter state code (e.g. CA, NY)"),
},
},
async ({ state }) => {
const stateCode = state.toUpperCase();
const alertsUrl = `${NWS_API_BASE}/alerts?area=${stateCode}`;
const alertsData = await makeNWSRequest<AlertsResponse>(alertsUrl);
if (!alertsData) {
return {
content: [
{
type: "text",
text: "Failed to retrieve alerts data",
},
],
};
}
const features = alertsData.features || [];
if (features.length === 0) {
return {
content: [
{
type: "text",
text: `No active alerts for ${stateCode}`,
},
],
};
}
const formattedAlerts = features.map(formatAlert);
const alertsText = `Active alerts for ${stateCode}:\n\n${formattedAlerts.join("\n")}`;
return {
content: [
{
type: "text",
text: alertsText,
},
],
};
},
);
server.registerTool(
"get_forecast",
{
description: "Get weather forecast for a location",
inputSchema: {
latitude: z
.number()
.min(-90)
.max(90)
.describe("Latitude of the location"),
longitude: z
.number()
.min(-180)
.max(180)
.describe("Longitude of the location"),
},
},
async ({ latitude, longitude }) => {
// Get grid point data
const pointsUrl = `${NWS_API_BASE}/points/${latitude.toFixed(4)},${longitude.toFixed(4)}`;
const pointsData = await makeNWSRequest<PointsResponse>(pointsUrl);
if (!pointsData) {
return {
content: [
{
type: "text",
text: `Failed to retrieve grid point data for coordinates: ${latitude}, ${longitude}. This location may not be supported by the NWS API (only US locations are supported).`,
},
],
};
}
const forecastUrl = pointsData.properties?.forecast;
if (!forecastUrl) {
return {
content: [
{
type: "text",
text: "Failed to get forecast URL from grid point data",
},
],
};
}
// Get forecast data
const forecastData = await makeNWSRequest<ForecastResponse>(forecastUrl);
if (!forecastData) {
return {
content: [
{
type: "text",
text: "Failed to retrieve forecast data",
},
],
};
}
const periods = forecastData.properties?.periods || [];
if (periods.length === 0) {
return {
content: [
{
type: "text",
text: "No forecast periods available",
},
],
};
}
// Format forecast periods
const formattedForecast = periods.map((period: ForecastPeriod) =>
[
`${period.name || "Unknown"}:`,
`Temperature: ${period.temperature || "Unknown"}°${period.temperatureUnit || "F"}`,
`Wind: ${period.windSpeed || "Unknown"} ${period.windDirection || ""}`,
`${period.shortForecast || "No forecast available"}`,
"---",
].join("\n"),
);
const forecastText = `Forecast for ${latitude}, ${longitude}:\n\n${formattedForecast.join("\n")}`;
return {
content: [
{
type: "text",
text: forecastText,
},
],
};
},
);运行服务器
最后,实现 main 函数来运行服务器:
async function main() {
const transport = new StdioServerTransport();
await server.connect(transport);
console.error("Weather MCP Server running on stdio");
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error("Fatal error in main():", error);
process.exit(1);
});确保运行 npm run build 来构建你的服务器!这是让服务器连接的重要步骤。
现在让我们从现有的 MCP 主机 Claude 桌面版测试你的服务器。
Testing your server with Claude for Desktop
Claude for Desktop is not yet available on Linux. Linux users can proceed to the Building a client tutorial to build an MCP client that connects to the server we just built.
First, make sure you have Claude for Desktop installed. You can install the latest version here. If you already have Claude for Desktop, make sure it’s updated to the latest version.
We’ll need to configure Claude for Desktop for whichever MCP servers you want to use. To do this, open your Claude for Desktop App configuration at ~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json in a text editor. Make sure to create the file if it doesn’t exist.
For example, if you have VS Code installed:
code ~/Library/Application\ Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.jsoncode $env:AppData\Claude\claude_desktop_config.json然后,你将在 mcpServers 键中添加服务器。只有在至少有一个服务器正确配置后,MCP UI 元素才会显示在 Claude 桌面版中。
在这种情况下,我们将像这样添加单个天气服务器:
{
"mcpServers": {
"weather": {
"command": "node",
"args": ["/ABSOLUTE/PATH/TO/PARENT/FOLDER/weather/build/index.js"]
}
}
}{
"mcpServers": {
"weather": {
"command": "node",
"args": ["C:\\PATH\\TO\\PARENT\\FOLDER\\weather\\build\\index.js"]
}
}
}This tells Claude for Desktop:
- There’s an MCP server named “weather”
- Launch it by running
node /ABSOLUTE/PATH/TO/PARENT/FOLDER/weather/build/index.js
Save the file, and restart Claude for Desktop.
This is a quickstart demo based on Spring AI MCP auto-configuration and boot starters. To learn how to create sync and async MCP Servers, manually, consult the Java SDK Server documentation.
Let’s get started with building our weather server! You can find the complete code for what we’ll be building here.
For more information, see the MCP Server Boot Starter reference documentation. For manual MCP Server implementation, refer to the MCP Server Java SDK documentation.
Logging in MCP Servers
When implementing MCP servers, be careful about how you handle logging:
For STDIO-based servers: Never write to standard output (stdout). This includes:
print()statements in Pythonconsole.log()in JavaScriptfmt.Println()in Go- Similar stdout functions in other languages
Writing to stdout will corrupt the JSON-RPC messages and break your server.
For HTTP-based servers: Standard output logging is fine since it doesn’t interfere with HTTP responses.
Best Practices
- Use a logging library that writes to stderr or files.
- Ensure any configured logging library will not write to STDOUT
System requirements
- Java 17 or higher installed.
- Spring Boot 3.3.x or higher
Set up your environment
Use the Spring Initializer to bootstrap the project.
You will need to add the following dependencies:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-starter-mcp-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>dependencies {
implementation platform("org.springframework.ai:spring-ai-starter-mcp-server")
implementation platform("org.springframework:spring-web")
}Then configure your application by setting the application properties:
spring.main.bannerMode=off
logging.pattern.console=logging:
pattern:
console:
spring:
main:
banner-mode: offThe Server Configuration Properties documents all available properties.
Now let’s dive into building your server.
构建服务器
天气服务
让我们实现一个 WeatherService.java,使用 REST 客户端从国家气象局 API 查询数据:
@Service
public class WeatherService {
private final RestClient restClient;
public WeatherService() {
this.restClient = RestClient.builder()
.baseUrl("https://api.weather.gov")
.defaultHeader("Accept", "application/geo+json")
.defaultHeader("User-Agent", "WeatherApiClient/1.0 ([email protected])")
.build();
}
@Tool(description = "Get weather forecast for a specific latitude/longitude")
public String getWeatherForecastByLocation(
double latitude, // Latitude coordinate
double longitude // Longitude coordinate
) {
// Returns detailed forecast including:
// - Temperature and unit
// - Wind speed and direction
// - Detailed forecast description
}
@Tool(description = "Get weather alerts for a US state")
public String getAlerts(
@ToolParam(description = "Two-letter US state code (e.g. CA, NY)") String state
) {
// Returns active alerts including:
// - Event type
// - Affected area
// - Severity
// - Description
// - Safety instructions
}
// ......
}@Service 注解将在你的应用程序上下文中自动注册服务。
Spring AI @Tool 注解使得创建和维护 MCP 工具变得容易。
自动配置将自动向 MCP 服务器注册这些工具。
创建 Boot 应用程序
@SpringBootApplication
public class McpServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(McpServerApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public ToolCallbackProvider weatherTools(WeatherService weatherService) {
return MethodToolCallbackProvider.builder().toolObjects(weatherService).build();
}
}使用 MethodToolCallbackProvider 工具将 @Tools 转换为 MCP 服务器使用的可操作回调。
运行服务器
最后,让我们构建服务器:
./mvnw clean install这将在 target 文件夹中生成 mcp-weather-stdio-server-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar 文件。
现在让我们从现有的 MCP 主机 Claude 桌面版测试你的服务器。
使用 Claude 桌面版测试服务器
Claude 桌面版尚不支持 Linux。
首先,确保已安装 Claude 桌面版。 你可以在此处安装最新版本。如果已有 Claude 桌面版,请确保更新到最新版本。
我们需要为要使用的任何 MCP 服务器配置 Claude 桌面版。
为此,请在文本编辑器中打开 ~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json 中的 Claude 桌面版应用配置。
如果文件不存在,请确保创建它。
例如,如果安装了 VS Code:
code ~/Library/Application\ Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.jsoncode $env:AppData\Claude\claude_desktop_config.jsonYou’ll then add your servers in the mcpServers key.
The MCP UI elements will only show up in Claude for Desktop if at least one server is properly configured.
In this case, we’ll add our single weather server like so:
{
"mcpServers": {
"spring-ai-mcp-weather": {
"command": "java",
"args": [
"-Dspring.ai.mcp.server.stdio=true",
"-jar",
"/ABSOLUTE/PATH/TO/PARENT/FOLDER/mcp-weather-stdio-server-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar"
]
}
}
}{
"mcpServers": {
"spring-ai-mcp-weather": {
"command": "java",
"args": [
"-Dspring.ai.mcp.server.transport=STDIO",
"-jar",
"C:\\ABSOLUTE\\PATH\\TO\\PARENT\\FOLDER\\weather\\mcp-weather-stdio-server-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar"
]
}
}
}确保传入服务器的绝对路径。
这告诉 Claude 桌面版:
- 有一个名为 “my-weather-server” 的 MCP 服务器
- 通过运行
java -jar /ABSOLUTE/PATH/TO/PARENT/FOLDER/mcp-weather-stdio-server-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar来启动它
保存文件,并重启 Claude 桌面版。
使用 Java 客户端测试服务器
手动创建 MCP 客户端
使用 McpClient 连接到服务器:
var stdioParams = ServerParameters.builder("java")
.args("-jar", "/ABSOLUTE/PATH/TO/PARENT/FOLDER/mcp-weather-stdio-server-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar")
.build();
var stdioTransport = new StdioClientTransport(stdioParams);
var mcpClient = McpClient.sync(stdioTransport).build();
mcpClient.initialize();
ListToolsResult toolsList = mcpClient.listTools();
CallToolResult weather = mcpClient.callTool(
new CallToolRequest("getWeatherForecastByLocation",
Map.of("latitude", "47.6062", "longitude", "-122.3321")));
CallToolResult alert = mcpClient.callTool(
new CallToolRequest("getAlerts", Map.of("state", "NY")));
mcpClient.closeGracefully();使用 MCP Client Boot Starter
使用 spring-ai-starter-mcp-client 依赖项创建新的 boot starter 应用程序:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-starter-mcp-client</artifactId>
</dependency>并设置 spring.ai.mcp.client.stdio.servers-configuration 属性指向你的 claude_desktop_config.json。
你可以重用现有的 Anthropic 桌面版配置:
spring.ai.mcp.client.stdio.servers-configuration=file:PATH/TO/claude_desktop_config.json当你启动客户端应用程序时,自动配置将自动从 claude_desktop_config.json 创建 MCP 客户端。
有关更多信息,请参阅 MCP Client Boot Starters 参考文档。
更多 Java MCP 服务器示例
starter-webflux-server 演示了如何使用 SSE 传输创建 MCP 服务器。 它展示了如何使用 Spring Boot 的自动配置功能定义和注册 MCP 工具、资源和提示词。
让我们开始构建天气服务器!你可以在这里找到我们将要构建的完整代码。
前置知识
本快速入门假设你熟悉:
- Kotlin
- LLM(如 Claude)
系统要求
- 安装 Java 17 或更高版本。
设置环境
首先,让我们安装 java 和 gradle(如果尚未安装)。
你可以从 官方 Oracle JDK 网站下载 java。
验证你的 java 安装:
java --version现在,让我们创建并设置我们的项目:
# Create a new directory for our project
mkdir weather
cd weather
# Initialize a new kotlin project
gradle init# Create a new directory for our project
md weather
cd weather
# Initialize a new kotlin project
gradle init运行 gradle init 后,系统将为你提供用于创建项目的选项。
选择 Application 作为项目类型,Kotlin 作为编程语言,Java 17 作为 Java 版本。
或者,你可以使用 IntelliJ IDEA 项目向导创建 Kotlin 应用程序。
创建项目后,添加以下依赖项:
val mcpVersion = "0.4.0"
val slf4jVersion = "2.0.9"
val ktorVersion = "3.1.1"
dependencies {
implementation("io.modelcontextprotocol:kotlin-sdk:$mcpVersion")
implementation("org.slf4j:slf4j-nop:$slf4jVersion")
implementation("io.ktor:ktor-client-content-negotiation:$ktorVersion")
implementation("io.ktor:ktor-serialization-kotlinx-json:$ktorVersion")
}def mcpVersion = '0.3.0'
def slf4jVersion = '2.0.9'
def ktorVersion = '3.1.1'
dependencies {
implementation "io.modelcontextprotocol:kotlin-sdk:$mcpVersion"
implementation "org.slf4j:slf4j-nop:$slf4jVersion"
implementation "io.ktor:ktor-client-content-negotiation:$ktorVersion"
implementation "io.ktor:ktor-serialization-kotlinx-json:$ktorVersion"
}此外,将以下插件添加到你的构建脚本中:
plugins {
kotlin("plugin.serialization") version "your_version_of_kotlin"
id("com.gradleup.shadow") version "8.3.9"
}plugins {
id 'org.jetbrains.kotlin.plugin.serialization' version 'your_version_of_kotlin'
id 'com.gradleup.shadow' version '8.3.9'
}现在让我们开始构建服务器。
构建服务器
设置实例
添加服务器初始化函数:
// Main function to run the MCP server
fun `run mcp server`() {
// Create the MCP Server instance with a basic implementation
val server = Server(
Implementation(
name = "weather", // Tool name is "weather"
version = "1.0.0" // Version of the implementation
),
ServerOptions(
capabilities = ServerCapabilities(tools = ServerCapabilities.Tools(listChanged = true))
)
)
// Create a transport using standard IO for server communication
val transport = StdioServerTransport(
System.`in`.asInput(),
System.out.asSink().buffered()
)
runBlocking {
server.connect(transport)
val done = Job()
server.onClose {
done.complete()
}
done.join()
}
}天气 API 辅助函数
接下来,让我们添加函数和数据类,用于从国家气象局 API 查询和转换响应:
// Extension function to fetch forecast information for given latitude and longitude
suspend fun HttpClient.getForecast(latitude: Double, longitude: Double): List<String> {
val points = this.get("/points/$latitude,$longitude").body<Points>()
val forecast = this.get(points.properties.forecast).body<Forecast>()
return forecast.properties.periods.map { period ->
"""
${period.name}:
Temperature: ${period.temperature} ${period.temperatureUnit}
Wind: ${period.windSpeed} ${period.windDirection}
Forecast: ${period.detailedForecast}
""".trimIndent()
}
}
// Extension function to fetch weather alerts for a given state
suspend fun HttpClient.getAlerts(state: String): List<String> {
val alerts = this.get("/alerts/active/area/$state").body<Alert>()
return alerts.features.map { feature ->
"""
Event: ${feature.properties.event}
Area: ${feature.properties.areaDesc}
Severity: ${feature.properties.severity}
Description: ${feature.properties.description}
Instruction: ${feature.properties.instruction}
""".trimIndent()
}
}
@Serializable
data class Points(
val properties: Properties
) {
@Serializable
data class Properties(val forecast: String)
}
@Serializable
data class Forecast(
val properties: Properties
) {
@Serializable
data class Properties(val periods: List<Period>)
@Serializable
data class Period(
val number: Int, val name: String, val startTime: String, val endTime: String,
val isDaytime: Boolean, val temperature: Int, val temperatureUnit: String,
val temperatureTrend: String, val probabilityOfPrecipitation: JsonObject,
val windSpeed: String, val windDirection: String,
val shortForecast: String, val detailedForecast: String,
)
}
@Serializable
data class Alert(
val features: List<Feature>
) {
@Serializable
data class Feature(
val properties: Properties
)
@Serializable
data class Properties(
val event: String, val areaDesc: String, val severity: String,
val description: String, val instruction: String?,
)
}实现工具执行
工具执行处理器负责实际执行每个工具的逻辑。让我们添加它:
// Create an HTTP client with a default request configuration and JSON content negotiation
val httpClient = HttpClient {
defaultRequest {
url("https://api.weather.gov")
headers {
append("Accept", "application/geo+json")
append("User-Agent", "WeatherApiClient/1.0")
}
contentType(ContentType.Application.Json)
}
// Install content negotiation plugin for JSON serialization/deserialization
install(ContentNegotiation) { json(Json { ignoreUnknownKeys = true }) }
}
// Register a tool to fetch weather alerts by state
server.addTool(
name = "get_alerts",
description = """
Get weather alerts for a US state. Input is Two-letter US state code (e.g. CA, NY)
""".trimIndent(),
inputSchema = Tool.Input(
properties = buildJsonObject {
putJsonObject("state") {
put("type", "string")
put("description", "Two-letter US state code (e.g. CA, NY)")
}
},
required = listOf("state")
)
) { request ->
val state = request.arguments["state"]?.jsonPrimitive?.content
if (state == null) {
return@addTool CallToolResult(
content = listOf(TextContent("The 'state' parameter is required."))
)
}
val alerts = httpClient.getAlerts(state)
CallToolResult(content = alerts.map { TextContent(it) })
}
// Register a tool to fetch weather forecast by latitude and longitude
server.addTool(
name = "get_forecast",
description = """
Get weather forecast for a specific latitude/longitude
""".trimIndent(),
inputSchema = Tool.Input(
properties = buildJsonObject {
putJsonObject("latitude") { put("type", "number") }
putJsonObject("longitude") { put("type", "number") }
},
required = listOf("latitude", "longitude")
)
) { request ->
val latitude = request.arguments["latitude"]?.jsonPrimitive?.doubleOrNull
val longitude = request.arguments["longitude"]?.jsonPrimitive?.doubleOrNull
if (latitude == null || longitude == null) {
return@addTool CallToolResult(
content = listOf(TextContent("The 'latitude' and 'longitude' parameters are required."))
)
}
val forecast = httpClient.getForecast(latitude, longitude)
CallToolResult(content = forecast.map { TextContent(it) })
}运行服务器
最后,实现 main 函数来运行服务器:
fun main() = `run mcp server`()确保运行 ./gradlew build 来构建你的服务器。这是让服务器连接的重要步骤。
现在让我们从现有的 MCP 主机 Claude 桌面版测试你的服务器。
Testing your server with Claude for Desktop
Claude for Desktop is not yet available on Linux. Linux users can proceed to the Building a client tutorial to build an MCP client that connects to the server we just built.
First, make sure you have Claude for Desktop installed. You can install the latest version here. If you already have Claude for Desktop, make sure it’s updated to the latest version.
We’ll need to configure Claude for Desktop for whichever MCP servers you want to use.
To do this, open your Claude for Desktop App configuration at ~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json in a text editor.
Make sure to create the file if it doesn’t exist.
For example, if you have VS Code installed:
code ~/Library/Application\ Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.jsoncode $env:AppData\Claude\claude_desktop_config.jsonYou’ll then add your servers in the mcpServers key.
The MCP UI elements will only show up in Claude for Desktop if at least one server is properly configured.
In this case, we’ll add our single weather server like so:
{
"mcpServers": {
"weather": {
"command": "java",
"args": [
"-jar",
"/ABSOLUTE/PATH/TO/PARENT/FOLDER/weather/build/libs/weather-0.1.0-all.jar"
]
}
}
}{
"mcpServers": {
"weather": {
"command": "java",
"args": [
"-jar",
"C:\\PATH\\TO\\PARENT\\FOLDER\\weather\\build\\libs\\weather-0.1.0-all.jar"
]
}
}
}This tells Claude for Desktop:
- There’s an MCP server named “weather”
- Launch it by running
java -jar /ABSOLUTE/PATH/TO/PARENT/FOLDER/weather/build/libs/weather-0.1.0-all.jar
Save the file, and restart Claude for Desktop.
让我们开始构建天气服务器!你可以在这里找到我们将要构建的完整代码。
前置知识
本快速入门假设你熟悉:
- C#
- LLM(如 Claude)
- .NET 8 或更高版本
MCP 服务器中的日志记录
在实现 MCP 服务器时,请注意如何处理日志记录:
**对于基于 STDIO 的服务器:**切勿写入标准输出。这包括:
- Python 中的
print()语句 - JavaScript 中的
console.log() - Go 中的
fmt.Println() - 其他语言中类似的标准输出函数
写入标准输出会破坏 JSON-RPC 消息并导致服务器崩溃。
**对于基于 HTTP 的服务器:**标准输出日志是可以的,因为它不会干扰 HTTP 响应。
最佳实践
- 使用写入 stderr 或文件的日志库
系统要求
- 安装 .NET 8 SDK 或更高版本。
设置环境
首先,让我们安装 dotnet(如果尚未安装)。你可以从 官方 Microsoft .NET 网站下载 dotnet。验证你的 dotnet 安装:
dotnet --versionNow, let’s create and set up your project:
# Create a new directory for our project
mkdir weather
cd weather
# Initialize a new C# project
dotnet new console# Create a new directory for our project
mkdir weather
cd weather
# Initialize a new C# project
dotnet new console# Add the Model Context Protocol SDK NuGet package
dotnet add package ModelContextProtocol --prerelease
# Add the .NET Hosting NuGet package
dotnet add package Microsoft.Extensions.HostingNow let’s dive into building your server.
Building your server
Open the Program.cs file in your project and replace its contents with the following code:
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
using ModelContextProtocol;
using System.Net.Http.Headers;
var builder = Host.CreateEmptyApplicationBuilder(settings: null);
builder.Services.AddMcpServer()
.WithStdioServerTransport()
.WithToolsFromAssembly();
builder.Services.AddSingleton(_ =>
{
var client = new HttpClient() { BaseAddress = new Uri("https://api.weather.gov") };
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.UserAgent.Add(new ProductInfoHeaderValue("weather-tool", "1.0"));
return client;
});
var app = builder.Build();
await app.RunAsync();When creating the ApplicationHostBuilder, ensure you use CreateEmptyApplicationBuilder instead of CreateDefaultBuilder. This ensures that the server does not write any additional messages to the console. This is only necessary for servers using STDIO transport.
This code sets up a basic console application that uses the Model Context Protocol SDK to create an MCP server with standard I/O transport.
Weather API helper functions
Create an extension class for HttpClient which helps simplify JSON request handling:
using System.Text.Json;
internal static class HttpClientExt
{
public static async Task<JsonDocument> ReadJsonDocumentAsync(this HttpClient client, string requestUri)
{
using var response = await client.GetAsync(requestUri);
response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
return await JsonDocument.ParseAsync(await response.Content.ReadAsStreamAsync());
}
}Next, define a class with the tool execution handlers for querying and converting responses from the National Weather Service API:
using ModelContextProtocol.Server;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Globalization;
using System.Text.Json;
namespace QuickstartWeatherServer.Tools;
[McpServerToolType]
public static class WeatherTools
{
[McpServerTool, Description("Get weather alerts for a US state code.")]
public static async Task<string> GetAlerts(
HttpClient client,
[Description("The US state code to get alerts for.")] string state)
{
using var jsonDocument = await client.ReadJsonDocumentAsync($"/alerts/active/area/{state}");
var jsonElement = jsonDocument.RootElement;
var alerts = jsonElement.GetProperty("features").EnumerateArray();
if (!alerts.Any())
{
return "No active alerts for this state.";
}
return string.Join("\n--\n", alerts.Select(alert =>
{
JsonElement properties = alert.GetProperty("properties");
return $"""
Event: {properties.GetProperty("event").GetString()}
Area: {properties.GetProperty("areaDesc").GetString()}
Severity: {properties.GetProperty("severity").GetString()}
Description: {properties.GetProperty("description").GetString()}
Instruction: {properties.GetProperty("instruction").GetString()}
""";
}));
}
[McpServerTool, Description("Get weather forecast for a location.")]
public static async Task<string> GetForecast(
HttpClient client,
[Description("Latitude of the location.")] double latitude,
[Description("Longitude of the location.")] double longitude)
{
var pointUrl = string.Create(CultureInfo.InvariantCulture, $"/points/{latitude},{longitude}");
using var jsonDocument = await client.ReadJsonDocumentAsync(pointUrl);
var forecastUrl = jsonDocument.RootElement.GetProperty("properties").GetProperty("forecast").GetString()
?? throw new Exception($"No forecast URL provided by {client.BaseAddress}points/{latitude},{longitude}");
using var forecastDocument = await client.ReadJsonDocumentAsync(forecastUrl);
var periods = forecastDocument.RootElement.GetProperty("properties").GetProperty("periods").EnumerateArray();
return string.Join("\n---\n", periods.Select(period => $"""
{period.GetProperty("name").GetString()}
Temperature: {period.GetProperty("temperature").GetInt32()}°F
Wind: {period.GetProperty("windSpeed").GetString()} {period.GetProperty("windDirection").GetString()}
Forecast: {period.GetProperty("detailedForecast").GetString()}
"""));
}
}Running the server
Finally, run the server using the following command:
dotnet runThis will start the server and listen for incoming requests on standard input/output.
Testing your server with Claude for Desktop
Claude for Desktop is not yet available on Linux. Linux users can proceed to the Building a client tutorial to build an MCP client that connects to the server we just built.
First, make sure you have Claude for Desktop installed. You can install the latest version
here. If you already have Claude for Desktop, make sure it’s updated to the latest version.
We’ll need to configure Claude for Desktop for whichever MCP servers you want to use. To do this, open your Claude for Desktop App configuration at ~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json in a text editor. Make sure to create the file if it doesn’t exist.
For example, if you have VS Code installed:
code ~/Library/Application\ Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.jsoncode $env:AppData\Claude\claude_desktop_config.jsonYou’ll then add your servers in the mcpServers key. The MCP UI elements will only show up in Claude for Desktop if at least one server is properly configured.
In this case, we’ll add our single weather server like so:
{
"mcpServers": {
"weather": {
"command": "dotnet",
"args": ["run", "--project", "/ABSOLUTE/PATH/TO/PROJECT", "--no-build"]
}
}
}{
"mcpServers": {
"weather": {
"command": "dotnet",
"args": [
"run",
"--project",
"C:\\ABSOLUTE\\PATH\\TO\\PROJECT",
"--no-build"
]
}
}
}This tells Claude for Desktop:
- There’s an MCP server named “weather”
- Launch it by running
dotnet run /ABSOLUTE/PATH/TO/PROJECTSave the file, and restart Claude for Desktop.
Let’s get started with building our weather server! You can find the complete code for what we’ll be building here.
前置知识
本快速入门假设你熟悉:
- Rust 编程语言
- Rust 中的 async/await
- LLM(如 Claude)
MCP 服务器中的日志记录
在实现 MCP 服务器时,请注意如何处理日志记录:
**对于基于 STDIO 的服务器:**切勿写入标准输出。这包括:
- Python 中的
print()语句 - JavaScript 中的
console.log() - Rust 中的
println!() - 其他语言中类似的标准输出函数
写入标准输出会破坏 JSON-RPC 消息并导致服务器崩溃。
**对于基于 HTTP 的服务器:**标准输出日志是可以的,因为它不会干扰 HTTP 响应。
最佳实践
- 使用写入 stderr 或文件的日志库,例如 Rust 中的
tracing或log。 - 配置你的日志框架以避免标准输出。
快速示例
// ❌ 错误(STDIO)
println!("Processing request");
// ✅ 正确(STDIO)
use tracing::info;
info!("Processing request"); // 写入 stderr
系统要求
- 安装 Rust 1.70 或更高版本。
- Cargo(随 Rust 安装一起提供)。
设置环境
首先,让我们安装 Rust(如果尚未安装)。你可以从 rust-lang.org 安装 Rust:
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | sh# Download and run rustup-init.exe from https://rustup.rs/验证你的 Rust 安装:
rustc --version
cargo --version现在,让我们创建并设置我们的项目:
# Create a new Rust project
cargo new weather
cd weather# Create a new Rust project
cargo new weather
cd weather更新你的 Cargo.toml 以添加所需的依赖项:
[package]
name = "weather"
version = "0.1.0"
edition = "2024"
[dependencies]
rmcp = { version = "0.3", features = ["server", "macros", "transport-io"] }
tokio = { version = "1.46", features = ["full"] }
reqwest = { version = "0.12", features = ["json"] }
serde = { version = "1.0", features = ["derive"] }
serde_json = "1.0"
anyhow = "1.0"
tracing = "0.1"
tracing-subscriber = { version = "0.3", features = ["env-filter", "std", "fmt"] }现在让我们开始构建服务器。
构建服务器
导入包和常量
打开 src/main.rs 并在顶部添加这些导入和常量:
use anyhow::Result;
use rmcp::{
ServerHandler, ServiceExt,
handler::server::{router::tool::ToolRouter, tool::Parameters},
model::*,
schemars, tool, tool_handler, tool_router,
};
use serde::Deserialize;
use serde::de::DeserializeOwned;
const NWS_API_BASE: &str = "https://api.weather.gov";
const USER_AGENT: &str = "weather-app/1.0";rmcp crate 为 Rust 提供了模型上下文协议 SDK,具有服务器实现、过程宏和 stdio 传输功能。
数据结构
接下来,让我们定义数据结构,用于从国家气象局 API 反序列化响应:
#[derive(Debug, Deserialize)]
struct AlertsResponse {
features: Vec<AlertFeature>,
}
#[derive(Debug, Deserialize)]
struct AlertFeature {
properties: AlertProperties,
}
#[derive(Debug, Deserialize)]
struct AlertProperties {
event: Option<String>,
#[serde(rename = "areaDesc")]
area_desc: Option<String>,
severity: Option<String>,
description: Option<String>,
instruction: Option<String>,
}
#[derive(Debug, Deserialize)]
struct PointsResponse {
properties: PointsProperties,
}
#[derive(Debug, Deserialize)]
struct PointsProperties {
forecast: String,
}
#[derive(Debug, Deserialize)]
struct ForecastResponse {
properties: ForecastProperties,
}
#[derive(Debug, Deserialize)]
struct ForecastProperties {
periods: Vec<ForecastPeriod>,
}
#[derive(Debug, Deserialize)]
struct ForecastPeriod {
name: String,
temperature: i32,
#[serde(rename = "temperatureUnit")]
temperature_unit: String,
#[serde(rename = "windSpeed")]
wind_speed: String,
#[serde(rename = "windDirection")]
wind_direction: String,
#[serde(rename = "detailedForecast")]
detailed_forecast: String,
}现在定义 MCP 客户端将发送的请求类型:
#[derive(serde::Deserialize, schemars::JsonSchema)]
pub struct MCPForecastRequest {
latitude: f32,
longitude: f32,
}
#[derive(serde::Deserialize, schemars::JsonSchema)]
pub struct MCPAlertRequest {
state: String,
}辅助函数
添加用于发出 API 请求和格式化响应的辅助函数:
async fn make_nws_request<T: DeserializeOwned>(url: &str) -> Result<T> {
let client = reqwest::Client::new();
let rsp = client
.get(url)
.header(reqwest::header::USER_AGENT, USER_AGENT)
.header(reqwest::header::ACCEPT, "application/geo+json")
.send()
.await?
.error_for_status()?;
Ok(rsp.json::<T>().await?)
}
fn format_alert(feature: &AlertFeature) -> String {
let props = &feature.properties;
format!(
"Event: {}\nArea: {}\nSeverity: {}\nDescription: {}\nInstructions: {}",
props.event.as_deref().unwrap_or("Unknown"),
props.area_desc.as_deref().unwrap_or("Unknown"),
props.severity.as_deref().unwrap_or("Unknown"),
props
.description
.as_deref()
.unwrap_or("No description available"),
props
.instruction
.as_deref()
.unwrap_or("No specific instructions provided")
)
}
fn format_period(period: &ForecastPeriod) -> String {
format!(
"{}:\nTemperature: {}°{}\nWind: {} {}\nForecast: {}",
period.name,
period.temperature,
period.temperature_unit,
period.wind_speed,
period.wind_direction,
period.detailed_forecast
)
}实现 Weather 服务器和工具
现在让我们实现带有工具处理程序的主要 Weather 服务器结构:
pub struct Weather {
tool_router: ToolRouter<Weather>,
}
#[tool_router]
impl Weather {
fn new() -> Self {
Self {
tool_router: Self::tool_router(),
}
}
#[tool(description = "Get weather alerts for a US state.")]
async fn get_alerts(
&self,
Parameters(MCPAlertRequest { state }): Parameters<MCPAlertRequest>,
) -> String {
let url = format!(
"{}/alerts/active/area/{}",
NWS_API_BASE,
state.to_uppercase()
);
match make_nws_request::<AlertsResponse>(&url).await {
Ok(data) => {
if data.features.is_empty() {
"No active alerts for this state.".to_string()
} else {
data.features
.iter()
.map(format_alert)
.collect::<Vec<_>>()
.join("\n---\n")
}
}
Err(_) => "Unable to fetch alerts or no alerts found.".to_string(),
}
}
#[tool(description = "Get weather forecast for a location.")]
async fn get_forecast(
&self,
Parameters(MCPForecastRequest {
latitude,
longitude,
}): Parameters<MCPForecastRequest>,
) -> String {
let points_url = format!("{NWS_API_BASE}/points/{latitude},{longitude}");
let Ok(points_data) = make_nws_request::<PointsResponse>(&points_url).await else {
return "Unable to fetch forecast data for this location.".to_string();
};
let forecast_url = points_data.properties.forecast;
let Ok(forecast_data) = make_nws_request::<ForecastResponse>(&forecast_url).await else {
return "Unable to fetch forecast data for this location.".to_string();
};
let periods = &forecast_data.properties.periods;
let forecast_summary: String = periods
.iter()
.take(5) // Next 5 periods only
.map(format_period)
.collect::<Vec<String>>()
.join("\n---\n");
forecast_summary
}
}The #[tool_router] macro automatically generates the routing logic, and the #[tool] attribute marks methods as MCP tools.
Implementing the ServerHandler
Implement the ServerHandler trait to define server capabilities:
#[tool_handler]
impl ServerHandler for Weather {
fn get_info(&self) -> ServerInfo {
ServerInfo {
capabilities: ServerCapabilities::builder().enable_tools().build(),
..Default::default()
}
}
}Running the server
Finally, implement the main function to run the server with stdio transport:
#[tokio::main]
async fn main() -> Result<()> {
let transport = (tokio::io::stdin(), tokio::io::stdout());
let service = Weather::new().serve(transport).await?;
service.waiting().await?;
Ok(())
}使用以下命令构建你的服务器:
cargo build --release编译后的二进制文件将在 target/release/weather 中。
现在让我们从现有的 MCP 主机 Claude 桌面版测试你的服务器。
使用 Claude 桌面版测试服务器
Claude 桌面版尚不支持 Linux。Linux 用户可以继续阅读构建客户端教程,构建一个连接到我们刚刚构建的服务器的 MCP 客户端。
首先,确保已安装 Claude 桌面版。你可以在此处安装最新版本。如果已有 Claude 桌面版,请确保更新到最新版本。
我们需要为要使用的任何 MCP 服务器配置 Claude 桌面版。为此,请在文本编辑器中打开 ~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json 中的 Claude 桌面版应用配置。如果文件不存在,请确保创建它。
例如,如果安装了 VS Code:
code ~/Library/Application\ Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.jsoncode $env:AppData\Claude\claude_desktop_config.json然后,你将在 mcpServers 键中添加服务器。只有在至少有一个服务器正确配置后,MCP UI 元素才会显示在 Claude 桌面版中。
在这种情况下,我们将像这样添加单个天气服务器:
{
"mcpServers": {
"weather": {
"command": "/ABSOLUTE/PATH/TO/PARENT/FOLDER/weather/target/release/weather"
}
}
}{
"mcpServers": {
"weather": {
"command": "C:\\ABSOLUTE\\PATH\\TO\\PARENT\\FOLDER\\weather\\target\\release\\weather.exe"
}
}
}确保传入编译后的二进制文件的绝对路径。你可以通过在 macOS/Linux 上从项目目录运行 pwd 或在 Windows 命令提示符上运行 cd 来获取此路径。在 Windows 上,请记住在 JSON 路径中使用双反斜杠 (\\) 或正斜杠 (/),并添加 .exe 扩展名。
这告诉 Claude 桌面版:
- 有一个名为 “weather” 的 MCP 服务器
- 通过运行指定路径下的编译后的二进制文件来启动它
保存文件,并重启 Claude 桌面版。
使用命令进行测试
让我们确保 Claude 桌面版能够识别我们在 weather 服务器中暴露的两个工具。你可以通过查找 “添加文件、连接器等 /” <img src="/images/claude-add-files-connectors-and-more.png" style={{display: ‘inline’, margin: 0, height: ‘1.3em’}} /> 图标来实现此目的:
After clicking on the plus icon, hover over the “Connectors” menu. You should see the weather servers listed:

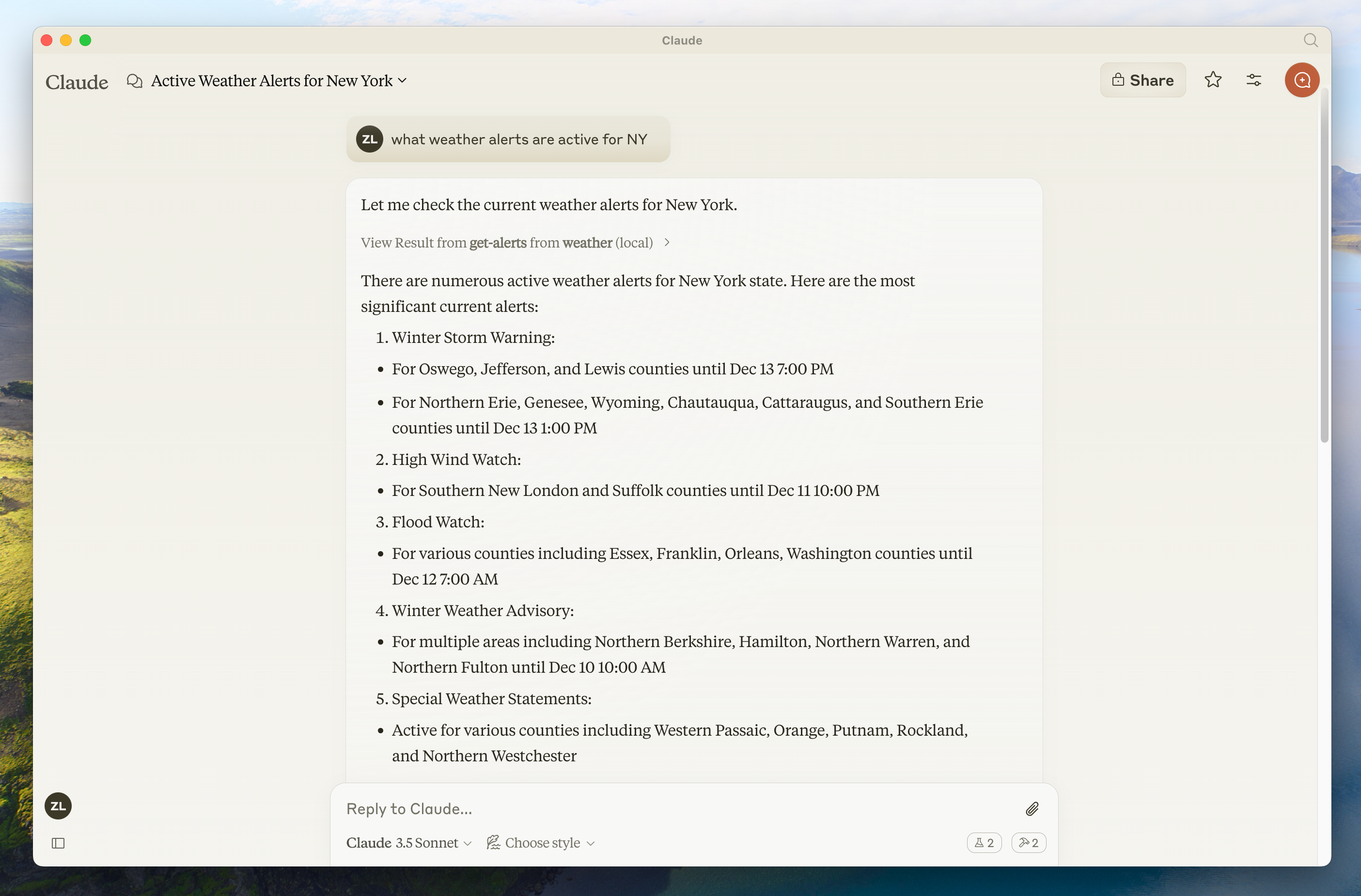
如果你的服务器未被 Claude 桌面版识别,请继续阅读故障排除部分以获取调试提示。
如果服务器已显示在"连接器"菜单中,你现在可以通过在 Claude 桌面版中运行以下命令来测试你的服务器:
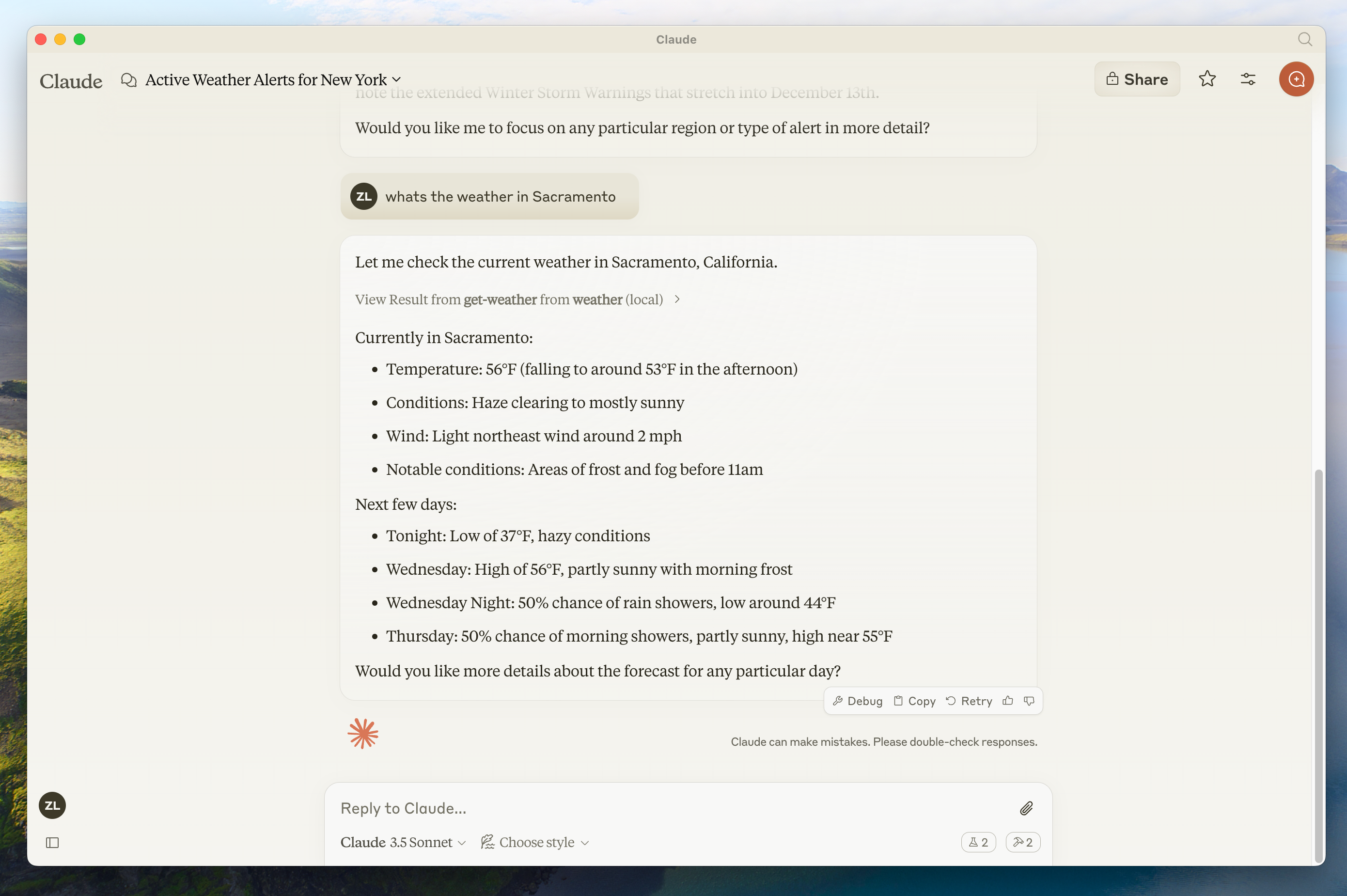
- 萨克拉门托的天气怎么样?
- 德克萨斯州有哪些活跃的天气警报?

由于这是美国国家气象服务,查询仅对美国位置有效。
底层发生了什么
当你提问时:
- 客户端将你的问题发送给 Claude
- Claude 分析可用工具并决定使用哪个工具
- 客户端通过 MCP 服务器执行所选工具
- 结果发送回 Claude
- Claude 构思自然语言响应
- 响应显示给你!
故障排除
从 Claude 桌面版获取日志
与 MCP 相关的 Claude.app 日志被写入 ~/Library/Logs/Claude 中的日志文件:
mcp.log将包含关于 MCP 连接和连接失败的一般日志。- 名为
mcp-server-SERVERNAME.log的文件将包含来自命名服务器的错误(stderr)日志。
你可以运行以下命令来列出最近的日志并跟随任何新日志:
# Check Claude's logs for errors
tail -n 20 -f ~/Library/Logs/Claude/mcp*.log服务器未显示在 Claude 中
- 检查你的
claude_desktop_config.json文件语法 - 确保你的项目路径是绝对路径而不是相对路径
- 完全重启 Claude 桌面版
要正确重启 Claude 桌面版,你必须完全退出应用程序:
- Windows:右键单击系统托盘中的 Claude 图标(可能隐藏在"隐藏图标"菜单中)并选择"退出"或"Exit"。
- macOS:使用 Cmd+Q 或从菜单栏中选择"退出 Claude"。
仅关闭窗口不会完全退出应用程序,你的 MCP 服务器配置更改也不会生效。
工具调用静默失败
如果 Claude 尝试使用工具但失败:
- 检查 Claude 的日志中是否有错误
- 验证你的服务器构建和运行没有错误
- 尝试重启 Claude 桌面版
这些都不起作用。我该怎么办?
请参阅我们的调试指南以获取更好的调试工具和更详细的指导。
错误:无法获取网格点数据
这通常意味着:
- 坐标在美国之外
- NWS API 出现问题
- 你被限速了
修复:
- 验证你使用的是美国坐标
- 在请求之间添加小延迟
- 检查 NWS API 状态页面
错误:[州] 没有活跃警报
这不是错误——只是意味着该州目前没有天气警报。尝试不同的州或在恶劣天气期间检查。
有关更高级的故障排除,请查看我们的 调试 MCP 指南