빠른 시작
이 튜토리얼에서는 간단한 MCP 날씨 서버를 구축하고 Claude for Desktop 호스트에 연결해 보겠습니다. 기본 설정부터 시작하여 더 복잡한 사용 사례로 진행할 것입니다.
구축할 내용
많은 LLM(Claude 포함)은 현재 예보 및 심각한 날씨 경보를 가져오는 기능이 없습니다. MCP를 사용하여 이 문제를 해결해 보겠습니다!
get-alerts와 get-forecast라는 두 가지 도구를 제공하는 서버를 구축할 것입니다. 그런 다음 이 서버를 MCP 호스트(이 경우 Claude for Desktop)에 연결하겠습니다:
왜 Claude.ai가 아닌 Claude for Desktop인가요?
MCP 핵심 개념
MCP 서버는 세 가지 주요 유형의 기능을 제공할 수 있습니다:
- 리소스(Resources): 클라이언트가 읽을 수 있는 파일과 유사한 데이터(API 응답이나 파일 내용 등)
- 도구(Tools): LLM이 호출할 수 있는 함수(사용자 승인 필요)
- 프롬프트(Prompts): 사용자가 특정 작업을 완료하는 데 도움이 되는 미리 작성된 템플릿
이 튜토리얼은 도구에 초점을 맞추고 있지만, 리소스와 프롬프트에 대해 더 알고 싶다면 중급 튜토리얼도 있습니다.
사전 지식
이 빠른 시작은 다음에 대한 익숙함을 가정합니다:
- Python
- Claude와 같은 LLM
시스템 요구사항
Python의 경우 Python 3.9 이상이 설치되어 있는지 확인하세요.
환경 설정
먼저 uv를 설치하고 Python 프로젝트와 환경을 설정해 보겠습니다:
curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | shpowershell -ExecutionPolicy ByPass -c "irm https://astral.sh/uv/install.ps1 | iex"uv 명령어가 인식되도록 터미널을 다시 시작해야 합니다.
이제 프로젝트를 생성하고 설정해 보겠습니다:
가상 환경 생성 및 활성화
uv venv source .venv/bin/activate
의존성 설치
uv add mcp httpx
템플릿 파일 제거
rm hello.py
파일 생성
mkdir -p src/weather touch src/weather/init.py touch src/weather/server.py
```powershell Windows
# 프로젝트를 위한 새 디렉토리 생성
uv init weather
cd weather
# 가상 환경 생성 및 활성화
uv venv
.venv\Scripts\activate
# 의존성 설치
uv add mcp httpx
# 상용구 코드 정리
rm hello.py
# 파일 생성
md src
md src\weather
new-item src\weather\__init__.py
new-item src\weather\server.py이 코드를 pyproject.toml에 추가하세요:
...나머지 구성
[build-system]
requires = [ "hatchling",]
build-backend = "hatchling.build"
[project.scripts]
weather = "weather:main"이 코드를 __init__.py에 추가하세요:
from . import server
import asyncio
def main():
"""패키지의 메인 진입점."""
asyncio.run(server.main())
# 선택적으로 패키지 레벨에서 다른 중요 항목 노출
__all__ = ['main', 'server']이제 서버 구축을 시작해 보겠습니다.
서버 구축
패키지 가져오기
server.py 파일 상단에 이 내용을 추가하세요:
from typing import Any
import asyncio
import httpx
from mcp.server.models import InitializationOptions
import mcp.types as types
from mcp.server import NotificationOptions, Server
import mcp.server.stdio인스턴스 설정
서버 인스턴스와 NWS API의 기본 URL을 초기화하세요:
NWS_API_BASE = "https://api.weather.gov"
USER_AGENT = "weather-app/1.0"
server = Server("weather")도구 목록 구현
클라이언트에 사용 가능한 도구를 알려줘야 합니다. list_tools() 데코레이터가 이 핸들러를 등록합니다:
@server.list_tools()
async def handle_list_tools() -> list[types.Tool]:
"""
사용 가능한 도구 목록을 표시합니다.
각 도구는 JSON 스키마 유효성 검사를 사용하여 인수를 지정합니다.
"""
return [
types.Tool(
name="get-alerts",
description="주(state)에 대한 날씨 경보 가져오기",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"state": {
"type": "string",
"description": "두 글자 주 코드 (예: CA, NY)",
},
},
"required": ["state"],
},
),
types.Tool(
name="get-forecast",
description="위치에 대한 날씨 예보 가져오기",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"latitude": {
"type": "number",
"description": "위치의 위도",
},
"longitude": {
"type": "number",
"description": "위치의 경도",
},
},
"required": ["latitude", "longitude"],
},
),
]이것이 get-alerts와 get-forecast라는 두 도구를 정의합니다.
헬퍼 함수
다음으로, National Weather Service API에서 데이터를 쿼리하고 포맷팅하기 위한 헬퍼 함수를 추가해 보겠습니다:
async def make_nws_request(client: httpx.AsyncClient, url: str) -> dict[str, Any] | None:
"""적절한 오류 처리로 NWS API에 요청을 보냅니다."""
headers = {
"User-Agent": USER_AGENT,
"Accept": "application/geo+json"
}
try:
response = await client.get(url, headers=headers, timeout=30.0)
response.raise_for_status()
return response.json()
except Exception:
return None
def format_alert(feature: dict) -> str:
"""경보 기능을 간결한 문자열로 포맷팅합니다."""
props = feature["properties"]
return (
f"이벤트: {props.get('event', 'Unknown')}\n"
f"지역: {props.get('areaDesc', 'Unknown')}\n"
f"심각도: {props.get('severity', 'Unknown')}\n"
f"상태: {props.get('status', 'Unknown')}\n"
f"헤드라인: {props.get('headline', 'No headline')}\n"
"---"
)도구 실행 구현
도구 실행 핸들러는 각 도구의 논리를 실제로 실행하는 역할을 합니다. 추가해 보겠습니다:
@server.call_tool()
async def handle_call_tool(
name: str, arguments: dict | None
) -> list[types.TextContent | types.ImageContent | types.EmbeddedResource]:
"""
도구 실행 요청을 처리합니다.
도구는 날씨 데이터를 가져오고 변경 사항을 클라이언트에 알릴 수 있습니다.
"""
if not arguments:
raise ValueError("인수가 누락되었습니다")
if name == "get-alerts":
state = arguments.get("state")
if not state:
raise ValueError("주(state) 매개변수가 누락되었습니다")
# 일관된 형식을 위해 주를 대문자로 변환
state = state.upper()
if len(state) != 2:
raise ValueError("주는 두 글자 코드여야 합니다 (예: CA, NY)")
async with httpx.AsyncClient() as client:
alerts_url = f"{NWS_API_BASE}/alerts?area={state}"
alerts_data = await make_nws_request(client, alerts_url)
if not alerts_data:
return [types.TextContent(type="text", text="경보 데이터를 가져오는 데 실패했습니다")]
features = alerts_data.get("features", [])
if not features:
return [types.TextContent(type="text", text=f"{state}에 활성 경보가 없습니다")]
# 각 경보를 간결한 문자열로 포맷팅
formatted_alerts = [format_alert(feature) for feature in features[:20]] # 처음 20개 경보만 가져옴
alerts_text = f"{state}의 활성 경보:\n\n" + "\n".join(formatted_alerts)
return [
types.TextContent(
type="text",
text=alerts_text
)
]
elif name == "get-forecast":
try:
latitude = float(arguments.get("latitude"))
longitude = float(arguments.get("longitude"))
except (TypeError, ValueError):
return [types.TextContent(
type="text",
text="잘못된 좌표입니다. 위도와 경도에 유효한 숫자를 제공해주세요."
)]
# 기본 좌표 유효성 검사
if not (-90 <= latitude <= 90) or not (-180 <= longitude <= 180):
return [types.TextContent(
type="text",
text="잘못된 좌표입니다. 위도는 -90에서 90 사이, 경도는 -180에서 180 사이여야 합니다."
)]
async with httpx.AsyncClient() as client:
# 먼저 그리드 포인트 가져오기
lat_str = f"{latitude}"
lon_str = f"{longitude}"
points_url = f"{NWS_API_BASE}/points/{lat_str},{lon_str}"
points_data = await make_nws_request(client, points_url)
if not points_data:
return [types.TextContent(type="text", text=f"좌표 {latitude}, {longitude}에 대한 그리드 포인트 데이터를 가져오는 데 실패했습니다. 이 위치는 NWS API에서 지원되지 않을 수 있습니다 (미국 위치만 지원됨).")]
# 응답에서 예보 URL 추출
properties = points_data.get("properties", {})
forecast_url = properties.get("forecast")
if not forecast_url:
return [types.TextContent(type="text", text="그리드 포인트 데이터에서 예보 URL을 가져오는 데 실패했습니다")]
# 예보 가져오기
forecast_data = await make_nws_request(client, forecast_url)
if not forecast_data:
return [types.TextContent(type="text", text="예보 데이터를 가져오는 데 실패했습니다")]
# 예보 기간 포맷팅
periods = forecast_data.get("properties", {}).get("periods", [])
if not periods:
return [types.TextContent(type="text", text="사용 가능한 예보 기간이 없습니다")]
# 각 기간을 간결한 문자열로 포맷팅
formatted_forecast = []
for period in periods:
forecast_text = (
f"{period.get('name', 'Unknown')}:\n"
f"온도: {period.get('temperature', 'Unknown')}°{period.get('temperatureUnit', 'F')}\n"
f"바람: {period.get('windSpeed', 'Unknown')} {period.get('windDirection', '')}\n"
f"{period.get('shortForecast', 'No forecast available')}\n"
"---"
)
formatted_forecast.append(forecast_text)
forecast_text = f"{latitude}, {longitude}의 예보:\n\n" + "\n".join(formatted_forecast)
return [types.TextContent(
type="text",
text=forecast_text
)]
else:
raise ValueError(f"알 수 없는 도구: {name}")서버 실행
마지막으로, 서버를 실행하기 위한 메인 함수를 구현하세요:
async def main():
# stdin/stdout 스트림을 사용하여 서버 실행
async with mcp.server.stdio.stdio_server() as (read_stream, write_stream):
await server.run(
read_stream,
write_stream,
InitializationOptions(
server_name="weather",
server_version="0.1.0",
capabilities=server.get_capabilities(
notification_options=NotificationOptions(),
experimental_capabilities={},
),
),
)
# 사용자 정의 클라이언트에 연결하려는 경우 필요합니다
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())서버가 완성되었습니다! uv run src/weather/server.py를 실행하여 모든 것이 작동하는지 확인하세요.
이제 기존 MCP 호스트인 Claude for Desktop에서 서버를 테스트해 보겠습니다.
Claude for Desktop으로 서버 테스트
먼저 Claude for Desktop이 설치되어 있는지 확인하세요. 여기서 최신 버전을 설치할 수 있습니다.
다음으로, 텍스트 편집기에서 ~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json에 있는 Claude for Desktop 앱 구성을 여세요.
예를 들어, VS Code가 설치된 경우:
code ~/Library/Application\ Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.jsoncode $env:AppData\Claude\claude_desktop_config.json이 구성을 추가하세요 (상위 폴더 경로를 교체):
{
"mcpServers": {
"weather": {
"command": "uv",
"args": [
"--directory",
"/절대/경로/상위/폴더/weather",
"run",
"weather"
]
}
}
}{
"mcpServers": {
"weather": {
"command": "uv",
"args": [
"--directory",
"C:\\절대\\경로\\상위\\폴더\\weather",
"run",
"weather"
]
}
}
}이것은 Claude for Desktop에 다음을 알려줍니다:
- “weather"라는 MCP 서버가 있습니다
uv --directory /절대/경로/상위/폴더/weather run weather를 실행하여 시작합니다
파일을 저장하고 Claude for Desktop을 다시 시작하세요.
사전 지식
이 빠른 시작은 다음에 대한 익숙함을 가정합니다:
- TypeScript
- Claude와 같은 LLM
시스템 요구사항
TypeScript의 경우 최신 버전의 Node가 설치되어 있는지 확인하세요.
환경 설정
먼저 Node.js와 npm을 설치하지 않았다면 설치하세요. nodejs.org에서 다운로드할 수 있습니다. Node.js 설치를 확인하세요:
node --version
npm --version이 튜토리얼의 경우 Node.js 버전 16 이상이 필요합니다.
이제 프로젝트를 생성하고 설정해 보겠습니다:
새 npm 프로젝트 초기화
npm init -y
의존성 설치
npm install @modelcontextprotocol/sdk zod npm install -D @types/node typescript
파일 생성
mkdir src touch src/index.ts
```powershell Windows
# 프로젝트를 위한 새 디렉토리 생성
md weather
cd weather
# 새 npm 프로젝트 초기화
npm init -y
# 의존성 설치
npm install @modelcontextprotocol/sdk zod
npm install -D @types/node typescript
# 파일 생성
md src
new-item src\index.tstype: “module"과 빌드 스크립트를 추가하도록 package.json을 업데이트하세요:
{
"type": "module",
"bin": {
"weather": "./build/index.js"
},
"scripts": {
"build": "tsc && node -e \"require('fs').chmodSync('build/index.js', '755')\"",
},
"files": [
"build"
],
}프로젝트 루트에 tsconfig.json을 생성하세요:
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "ES2022",
"module": "Node16",
"moduleResolution": "Node16",
"outDir": "./build",
"rootDir": "./src",
"strict": true,
"esModuleInterop": true,
"skipLibCheck": true,
"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true
},
"include": ["src/**/*"],
"exclude": ["node_modules"]
}이제 서버 구축을 시작해 보겠습니다.
서버 구축
패키지 가져오기
src/index.ts 상단에 이 내용을 추가하세요:
import { Server } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/index.js";
import { StdioServerTransport } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/stdio.js";
import {
CallToolRequestSchema,
ListToolsRequestSchema,
} from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/types.js";
import { z } from "zod";인스턴스 설정
NWS API 기본 URL, 유효성 검사 스키마, 서버 인스턴스를 초기화하세요:
const NWS_API_BASE = "https://api.weather.gov";
const USER_AGENT = "weather-app/1.0";
// 유효성 검사를 위한 Zod 스키마 정의
const AlertsArgumentsSchema = z.object({
state: z.string().length(2),
});
const ForecastArgumentsSchema = z.object({
latitude: z.number().min(-90).max(90),
longitude: z.number().min(-180).max(180),
});
// 서버 인스턴스 생성
const server = new Server(
{
name: "weather",
version: "1.0.0",
},
{
capabilities: {
tools: {},
},
}
);도구 목록 구현
클라이언트에 사용 가능한 도구를 알려줘야 합니다. 이 server.setRequestHandler 호출이 목록을 등록해 줍니다:
// 사용 가능한 도구 목록 표시
server.setRequestHandler(ListToolsRequestSchema, async () => {
return {
tools: [
{
name: "get-alerts",
description: "주(state)에 대한 날씨 경보 가져오기",
inputSchema: {
type: "object",
properties: {
state: {
type: "string",
description: "두 글자 주 코드 (예: CA, NY)",
},
},
required: ["state"],
},
},
{
name: "get-forecast",
description: "위치에 대한 날씨 예보 가져오기",
inputSchema: {
type: "object",
properties: {
latitude: {
type: "number",
description: "위치의 위도",
},
longitude: {
type: "number",
description: "위치의 경도",
},
},
required: ["latitude", "longitude"],
},
},
],
};
});이것이 get-alerts와 get-forecast라는 두 도구를 정의합니다.
헬퍼 함수
다음으로, National Weather Service API에서 데이터를 쿼리하고 포맷팅하기 위한 헬퍼 함수를 추가해 보겠습니다:
// NWS API 요청을 위한 헬퍼 함수
async function makeNWSRequest<T>(url: string): Promise<T | null> {
const headers = {
"User-Agent": USER_AGENT,
Accept: "application/geo+json",
};
try {
const response = await fetch(url, { headers });
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(`HTTP error! status: ${response.status}`);
}
return (await response.json()) as T;
} catch (error) {
console.error("NWS 요청 오류:", error);
return null;
}
}
interface AlertFeature {
properties: {
event?: string;
areaDesc?: string;
severity?: string;
status?: string;
headline?: string;
};
}
// 경보 데이터 포맷팅
function formatAlert(feature: AlertFeature): string {
const props = feature.properties;
return [
`이벤트: ${props.event || "Unknown"}`,
`지역: ${props.areaDesc || "Unknown"}`,
`심각도: ${props.severity || "Unknown"}`,
`상태: ${props.status || "Unknown"}`,
`헤드라인: ${props.headline || "No headline"}`,
"---",
].join("\n");
}
interface ForecastPeriod {
name?: string;
temperature?: number;
temperatureUnit?: string;
windSpeed?: string;
windDirection?: string;
shortForecast?: string;
}
interface AlertsResponse {
features: AlertFeature[];
}
interface PointsResponse {
properties: {
forecast?: string;
};
}
interface ForecastResponse {
properties: {
periods: ForecastPeriod[];
};
}도구 실행 구현
도구 실행 핸들러는 각 도구의 논리를 실제로 실행하는 역할을 합니다. 추가해 보겠습니다:
// 도구 실행 처리
server.setRequestHandler(CallToolRequestSchema, async (request) => {
const { name, arguments: args } = request.params;
try {
if (name === "get-alerts") {
const { state } = AlertsArgumentsSchema.parse(args);
const stateCode = state.toUpperCase();
const alertsUrl = `${NWS_API_BASE}/alerts?area=${stateCode}`;
const alertsData = await makeNWSRequest<AlertsResponse>(alertsUrl);
if (!alertsData) {
return {
content: [
{
type: "text",
text: "경보 데이터를 가져오는 데 실패했습니다",
},
],
};
}
const features = alertsData.features || [];
if (features.length === 0) {
return {
content: [
{
type: "text",
text: `${stateCode}에 활성 경보가 없습니다`,
},
],
};
}
const formattedAlerts = features.map(formatAlert).slice(0, 20) // 처음 20개 경보만 가져옴;
const alertsText = `${stateCode}의 활성 경보:\n\n${formattedAlerts.join(
"\n"
)}`;
return {
content: [
{
type: "text",
text: alertsText,
},
],
};
} else if (name === "get-forecast") {
const { latitude, longitude } = ForecastArgumentsSchema.parse(args);
// 그리드 포인트 데이터 가져오기
const pointsUrl = `${NWS_API_BASE}/points/${latitude.toFixed(
4
)},${longitude.toFixed(4)}`;
const pointsData = await makeNWSRequest<PointsResponse>(pointsUrl);
if (!pointsData) {
return {
content: [
{
type: "text",
text: `좌표 ${latitude}, ${longitude}에 대한 그리드 포인트 데이터를 가져오는 데 실패했습니다. 이 위치는 NWS API에서 지원되지 않을 수 있습니다 (미국 위치만 지원됨).`,
},
],
};
}
const forecastUrl = pointsData.properties?.forecast;
if (!forecastUrl) {
return {
content: [
{
type: "text",
text: "그리드 포인트 데이터에서 예보 URL을 가져오는 데 실패했습니다",
},
],
};
}
// 예보 데이터 가져오기
const forecastData = await makeNWSRequest<ForecastResponse>(forecastUrl);
if (!forecastData) {
return {
content: [
{
type: "text",
text: "예보 데이터를 가져오는 데 실패했습니다",
},
],
};
}
const periods = forecastData.properties?.periods || [];
if (periods.length === 0) {
return {
content: [
{
type: "text",
text: "사용 가능한 예보 기간이 없습니다",
},
],
};
}
// 예보 기간 포맷팅
const formattedForecast = periods.map((period: ForecastPeriod) =>
[
`${period.name || "Unknown"}:`,
`온도: ${period.temperature || "Unknown"}°${
period.temperatureUnit || "F"
}`,
`바람: ${period.windSpeed || "Unknown"} ${
period.windDirection || ""
}`,
`${period.shortForecast || "No forecast available"}`,
"---",
].join("\n")
);
const forecastText = `${latitude}, ${longitude}의 예보:\n\n${formattedForecast.join(
"\n"
)}`;
return {
content: [
{
type: "text",
text: forecastText,
},
],
};
} else {
throw new Error(`알 수 없는 도구: ${name}`);
}
} catch (error) {
if (error instanceof z.ZodError) {
throw new Error(
`잘못된 인수: ${error.errors
.map((e) => `${e.path.join(".")}: ${e.message}`)
.join(", ")}`
);
}
throw error;
}
});서버 실행
마지막으로, 서버를 실행하기 위한 메인 함수를 구현하세요:
// 서버 시작
async function main() {
const transport = new StdioServerTransport();
await server.connect(transport);
console.error("날씨 MCP 서버가 stdio에서 실행 중입니다");
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error("main()에서 치명적인 오류:", error);
process.exit(1);
});npm run build를 실행하여 서버를 빌드하는 것을 잊지 마세요! 이것은 서버 연결을 위해 매우 중요한 단계입니다.
이제 기존 MCP 호스트인 Claude for Desktop에서 서버를 테스트해 보겠습니다.
Claude for Desktop으로 서버 테스트
먼저 Claude for Desktop이 설치되어 있는지 확인하세요. 여기서 최신 버전을 설치할 수 있습니다.
다음으로, 텍스트 편집기에서 ~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json에 있는 Claude for Desktop 앱 구성을 여세요.
예를 들어, VS Code가 설치된 경우:
이 구성을 추가하세요 (상위 폴더 경로를 교체):
이것은 Claude for Desktop에 다음을 알려줍니다:
- “weather"라는 MCP 서버가 있습니다
node /절대/경로/상위/폴더/weather/build/index.js를 실행하여 시작합니다
파일을 저장하고 Claude for Desktop을 다시 시작하세요.
명령어로 테스트
먼저 Claude for Desktop이 weather 서버에서 노출한 두 도구를 인식하는지 확인하세요. 망치 <img src="/images/claude-desktop-mcp-hammer-icon.svg” style={{display: ‘inline’, margin: 0, height: ‘1.3em’}} /> 아이콘을 찾아볼 수 있습니다:
망치 아이콘을 클릭하면 두 개의 도구가 표시되어야 합니다:

서버가 Claude for Desktop에서 인식되지 않는다면, 디버깅 조언을 위해 문제 해결 섹션으로 진행하세요.
이제 Claude for Desktop에서 다음 명령어를 실행하여 서버를 테스트할 수 있습니다:
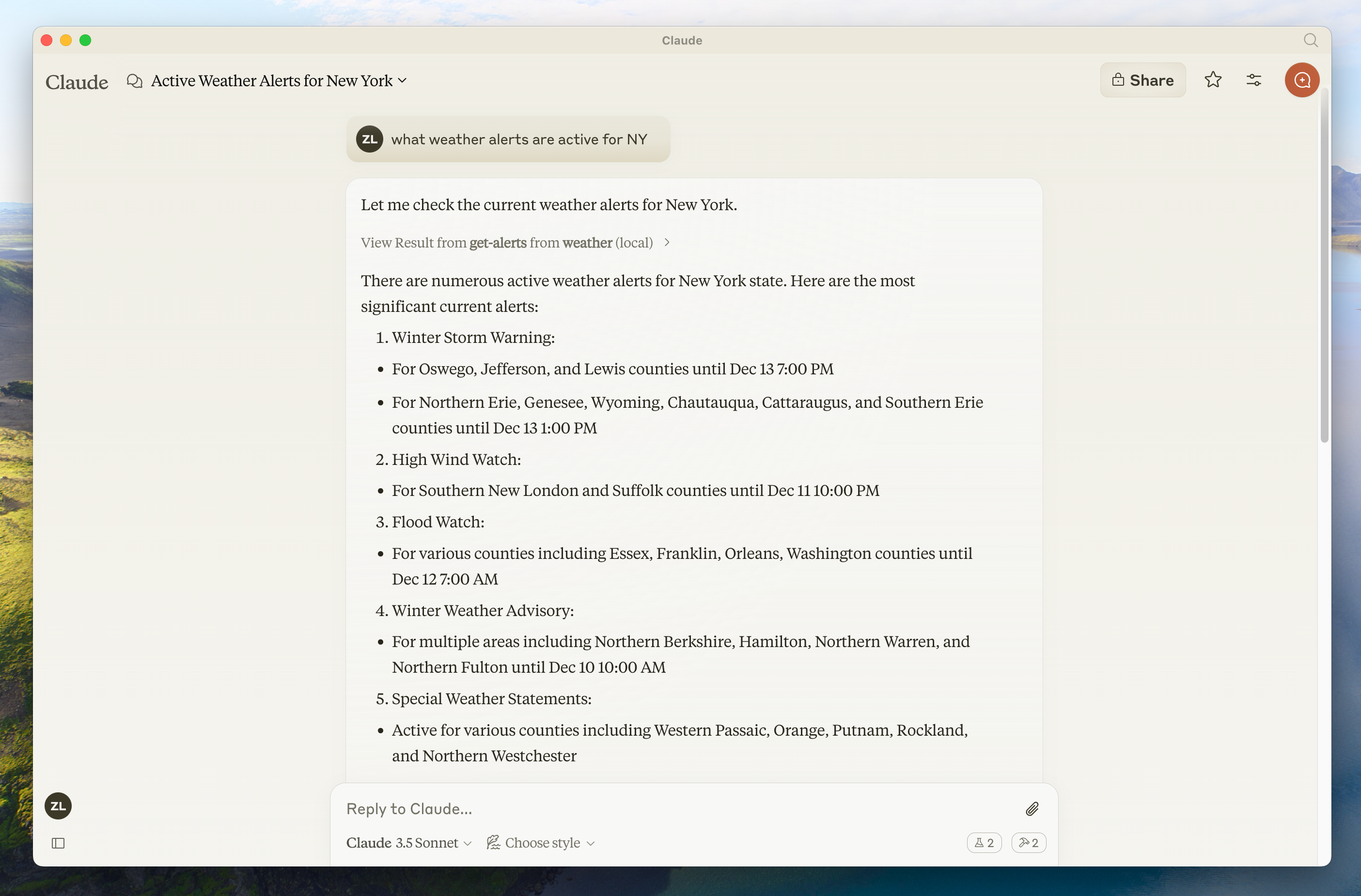
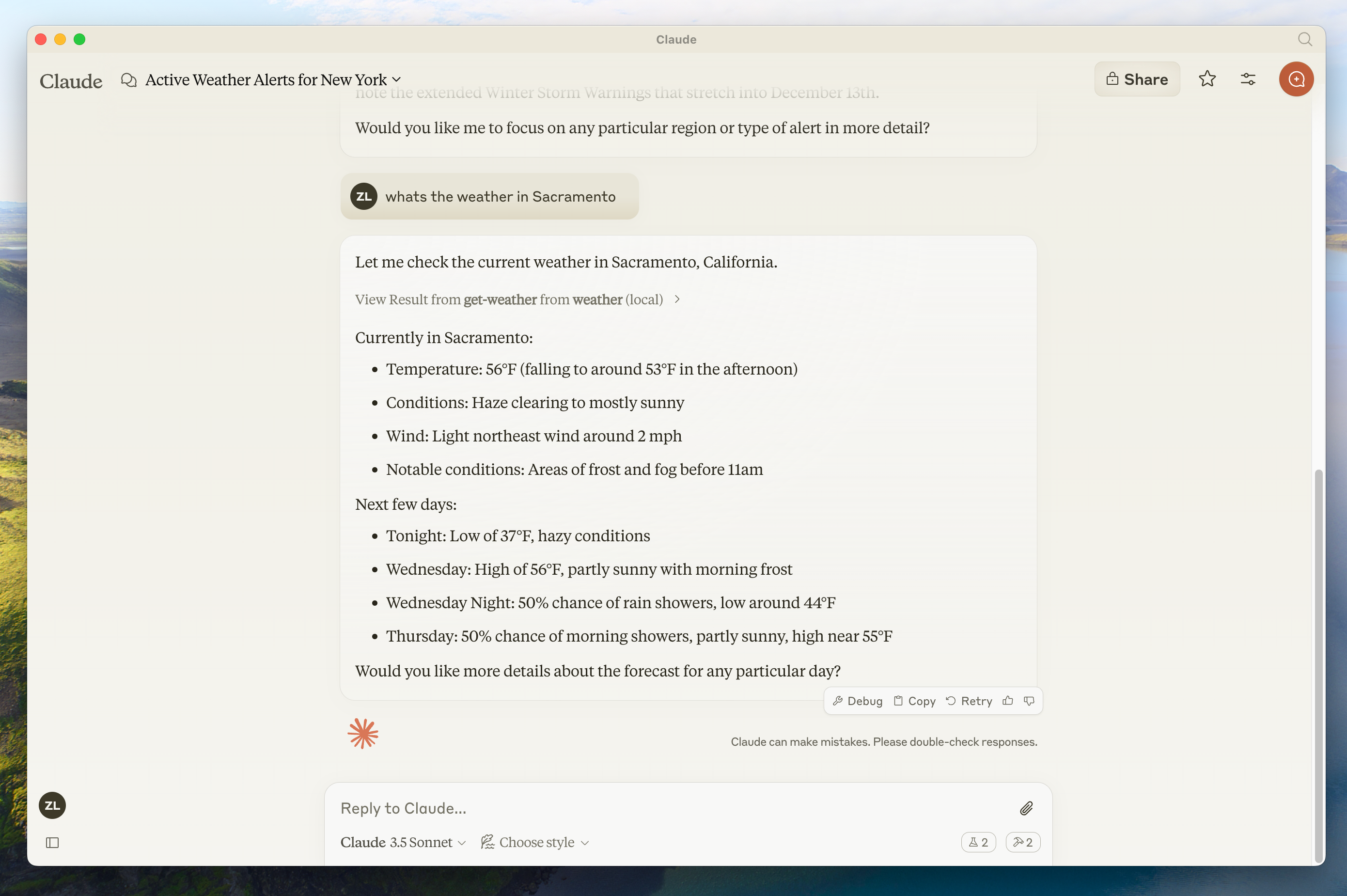
- 새크라멘토의 날씨는 어때요?
- 텍사스의 활성 날씨 경보는 무엇인가요?


내부에서 일어나는 일
질문을 할 때 다음과 같은 일이 발생합니다:
- 클라이언트가 질문을 Claude에 보냅니다
- Claude가 사용 가능한 도구를 분석하고 어떤 도구를 사용할지 결정합니다
- 클라이언트가 MCP 서버를 통해 선택된 도구를 실행합니다
- 결과가 Claude로 다시 전송됩니다
- Claude가 자연어 응답을 구성합니다
- 응답이 사용자에게 표시됩니다!
문제 해결
이것은 보통 다음을 의미합니다:
- 좌표가 미국 외부에 있습니다
- NWS API에 문제가 있습니다
- 속도 제한을 받고 있습니다
해결 방법:
- 미국 좌표를 사용하고 있는지 확인하세요
- 요청 사이에 작은 지연을 추가하세요
- NWS API 상태 페이지를 확인하세요
오류: [주]에 활성 경보가 없습니다
이것은 오류가 아닙니다 - 단지 해당 주에 현재 날씨 경보가 없다는 것을 의미합니다. 다른 주를 시도하거나 심각한 날씨 동안 확인해 보세요.
- 구성 파일 구문을 확인하세요
- 프로젝트 경로가 올바른지 확인하세요
- Claude for Desktop을 완전히 다시 시작하세요
다음과 같이 오류에 대한 Claude 로그를 확인할 수도 있습니다:
# 오류에 대한 Claude 로그 확인
tail -n 20 -f ~/Library/Logs/Claude/mcp*.log도구 호출이 조용히 실패함
Claude가 도구를 사용하려고 시도하지만 실패하는 경우:
- 오류에 대한 Claude 로그를 확인하세요
- 서버가 오류 없이 실행되는지 확인하세요
- Claude for Desktop을 다시 시작해 보세요